To meet durability targets a turbocharger needs coolant running through its system. The major advantage of liquid cooling is coolant can be circulated after hot engine shut down. Heat generated in the turbo housing and exhaust manifold soaks into the centre section of the turbocharger.

- Why do turbochargers need water cooling?
- Water-cooling improves mechanical durability and lengthens the turbocharger’s life. Many turbochargers are designed without water cooling ports and are sufficiently cooled by air and the lubricating oil that flows through them.
- How do you cool a turbo after it’s shut down?
- Second, they have developed ways to cool the turbo after the engine is shut down to alleviate heat soak. When the engine is running, the oil is a coolant that draws heat out of the turbocharger. But, for the oil to cool the turbo, it must flow. Restrictions in the oil feed or return lines can cause the turbocharger to operate hotter than normal.
- Can you cool a Garrett GTX Turbo with water?
- Garrett GTX and G Series ball bearing turbos are designed to be cooled by oil and water. Water cooling’s main benefit actually occurs after the engine has been shut down. Heat stored in the turbine housing and exhaust manifold “soaks back” into the center section of the turbocharger after shutdown.
- How does oil cool a turbocharger?
- But, for the oil to cool the turbo, it must flow. Restrictions in the oil feed or return lines can cause the turbocharger to operate hotter than normal. The most common restriction for turbochargers are not blockages in the feed line, but elevated crankcase pressure. The return line on most engines is plumbed into or above the oil pan.
Can you run a turbo without water?
Many turbochargers are designed without water cooling ports and are sufficiently cooled by air and the lubricating oil that flows through them. Other turbochargers, such as many in the Garrett® GT & GTX ball bearing line up, are designed from the beginning to be cooled by oil and water.

- Can a turbocharger be water cooled?
- Water-cooling a turbocharger does not need to be a complex project. The turbo’s water lines should be plumbed into the engine’s existing cooling system, and can be teed off of the heater lines if they are still present in the vehicle and convenient.
- Can I Run my engine without a turbo?
- You can totally run your engine without a turbo, but you need to do it right. I’ll assume your turbo is trash and you don’t want to pay to replace it. Understandable. You cooould replace your turbo with a custom made pipe from your exhaust manifold to the downpipe. Then you block off the oil feed and return hoses that went to the turbo.
- What happens if water is not plumbed in a turbocharger?
- Heat stored in the turbine housing and exhaust manifold “soaks back” into the center section of the turbocharger after shutdown. If water is not plumbed correctly, this intense heat can potentially destroy the bearing system and the oil-sealing piston rings behind the turbine wheel. Does my turbo really need water? Why should I care?
Is turbo better on gas?
Fuel efficiency: Because turbochargers give your car extra power without increasing the size of the engine, they’re typically more fuel-efficient than larger engines.
- Do turbocharged engines get better gas mileage?
- The latest turbocharged engines are smaller – in many cases very small. The new Ford Focus and Fiesta ST use 1.0-liter three-cylinder engines. Since the turbocharger only produces extra power and uses extra gas when it needs it, these smaller engines get better gas mileage when the driver is just cruising along than a bigger engine would.
- Does a turbo engine need gas?
- Because turbo engines compress more air in the cylinder, they may pre-detonate and have high chances of knocking. This will have a negative impact on the engine even though modern vehicles have an ECU to compensate for it. It is difficult to ignite premium gas in a turbocharged engine compared to regular gas. What Is the Best Gas for Turbo Engines?
- Why is premium gas a good choice for a turbo engine?
- Premium gas is suitable for turbo engines because it is hard to ignite since it has high octane levels. It is also ideal for running the engine at greater compression rations before detonation. By increasing the compression ratio, a turbocharger boosts the amount of gas in the cylinder, which results in a more efficient engine .
- Do turbochargers really work?
- Since the turbocharger only produces extra power and uses extra gas when it needs it, these smaller engines get better gas mileage when the driver is just cruising along than a bigger engine would. Their tiny turbochargers also spool up to speed quickly – more quickly than the whole engine could rev up to deliver similar power. Do They Work?
Why are turbos so hot?
Turbo chargers get hot because hot exhaust gases flow through the manifold then the turbo. So when the turbo is red hot, the manifold also glows with red heat. The temperature of the exhaust gas in diesel engines varies by manufacturer.

- Why does a turbo need a hot exhaust gas?
- A turbo needs enough exhaust gas to overcome its boost threshold, which both throttle position and engine rpm impact. The hot exhaust gas heats the turbo raising the intake air temperature. Hot air has decreased density and less oxygen than cold air, which causes reduced engine performance.
- What happens to a turbocharger in hot weather?
- Again, this serves to increase the amount of work the turbo has to do, reducing the overall efficiency and performance of your vehicle’s engine. For most people, the drop in turbocharger performance during hot weather won’t be a problem.
- How does a turbo boost work?
- Adding boost with a turbo increases the temperature of the charge air above inlet air temperature through compression of the air. This calculator provides the temperature of the air as it exits the turbo. If you are using an intercooler we have a calculator that will work out the temperature after the IC as well.
- How does hot air affect engine performance?
- The hot exhaust gas heats the turbo raising the intake air temperature. Hot air has decreased density and less oxygen than cold air, which causes reduced engine performance. Before air enters the engine, it travels through an intercooler to lower the intake air temperature.
Can water damage a turbo?
If water is not plumbed correctly, this intense heat can potentially destroy the bearing system and the oil-sealing piston ring behind the turbine wheel. Water ports are located on either side of the turbo’s center housing.
- Is it possible to damage a turbo at idle?
- Unfortunately, yes. The turbo is spinning at least 10,000 rpm even at idle. If it hits something like a paper towel or a signifigant amount of water, the turbo wheel usually touches the housing or the bearing gets ground up. Even if the damage isn’t immediate, it builds up since the turbo has to be balanced.
- What happens if a turbo wheel is damaged?
- If it hits something like a paper towel or a signifigant amount of water, the turbo wheel usually touches the housing or the bearing gets ground up. Even if the damage isn’t immediate, it builds up since the turbo has to be balanced. A damaged wheel will throw it out of balance and over time it will wobble until it finally snaps.
- Does water in a turbo cause coolant to leak?
- The water in a turbo allows you to safely shut the car off even after very recently boosting. The water mass absorbs the heat instead of the oil left in the CHRA having to do it so as not to get ‘oil coking’ damage to the shaft. Unless the casting is cracked then no, coolant won’t leak from there.
Do I need to let my turbo cool down?
Turbocharged engines do need to cool down before they are turned off. But in nearly all driving conditions, the engine does not reach temperatures that require a deliberate cooling down period.
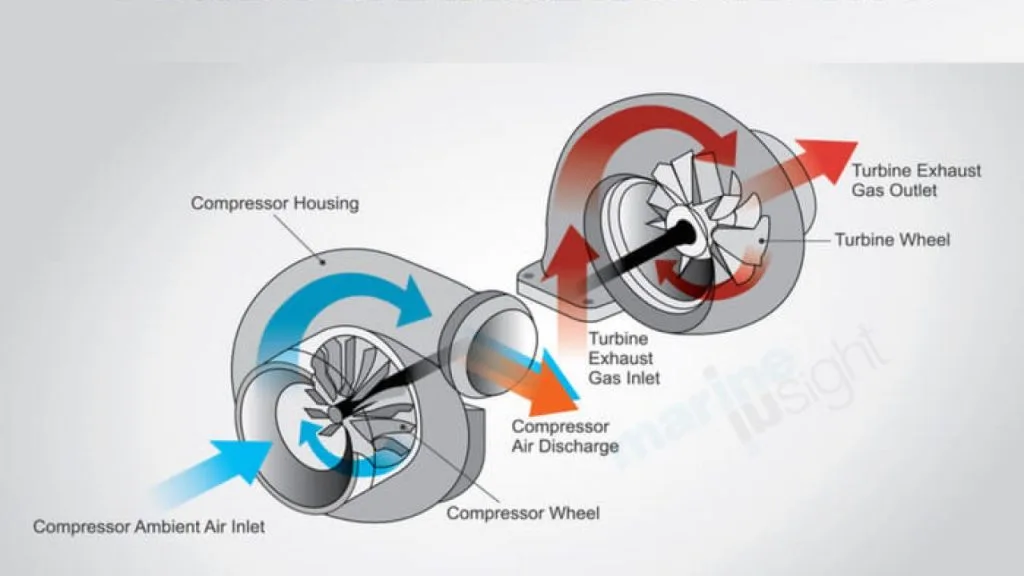
- Should I idle and cool down my turbocharged engine?
- You should idle and cool down your turbocharged engine because the oil in the bearing shaft can easily get burnt, and the residue can cause the turbo engine to fail. The other parts of the engine could also get damaged because the engine did not cool properly before the switch off.
- How do you keep a Turbo Cool?
- To keep them cool two methods are used, oil cooling and water cooling and sometimes both together, depending on tge size of the turbo and the thrust it generates. While you run the engine, the oil and coolent keep running through the engine and tge turbo.
- What temperature does a turbo cooled engine stay?
- So in a turbo charged engine, the engine will still remain around 80 degree Celsius (because it is constantly being cooled). How come the radiator/fan which cools the engine, can’t keep the turbo just as cool as well? Jul 22, 2015 at 12:19 The turbine side needs hot gases in order to make it spin really fast.
- How do I lubricate my turbo after hard driving?
- After hard driving, just drive your car slowly/calmly for a few miles. This will let the turbo cool down and because the engine is still on, the various turbo parts will still be lubricated whilst the turbo is cooling down. Not the answer you’re looking for?
Why do turbos like cold air?
As air temperature increases, the density of the air, and the amount of oxygen it holds decreases. This means that the turbocharger has to work harder, spin faster and compress more air to produce the same amount of boost it would at lower temperatures.
- How do I cool my Turbo?
- Fit a larger air intake – increasing the amount of air available to your turbo Replace your air filter – to ensure that it is clean and free flowing Fit a water or methanol injection system – which can be used to cool either the intake air, or the charged air.
- How does a turbo work?
- A turbo provides extra power because it uses the exhaust gases to pump air into the engine block under pressure. This technique is very effective and beside more power a turbo can decrease the fuel consumption. A turbo uses the exhaust gases to set a flywheel in motion, the more revs, the more exhaust gases the faster the flywheel turns.
- How does hotter air affect the turbocharger?
- In addition, hotter air also has a secondary affect on the turbocharger, by naturally increasing the operating temperature inside the turbo. Usually, the intercooler works to cool the air from the hot air intake, but in warmer temperatures, the intercooler becomes less efficient, as it is also exposed to the warmer temperatures.
- Why does a turbo make a loud noise?
- Turbos tend to make the air escaping the engine a little muffled, due in part to the fact that there are other noises happening, but mainly because of the fact that the turbo itself acts as a muffling chamber. The result is that the engine doesn’t scream as loudly and many of the natural tones of the engine itself are lost.
Should a turbo get really hot?
A turbocharger is exposed to very high temperatures because it uses exhaust gas energy. A normal gasoline engine can get up to 1,000 degrees hot. If the car is parked after a long full-throttle drive, especially after a long drive on the highway, a build-up of heat can form in the engine compartment.
- Should you buy a turbocharged engine?
- It’s essential to weigh the pros and cons when deciding if a turbocharged engine will be the right choice. Turbos make an excellent choice for drivers who value performance. They’re also great for drivers not willing to make a big sacrifice in fuel efficiency under everyday driving conditions.
- Why does my Turbo glow sooo red?
- last time i saw a turbo glow sooo red was because the socal supra owner drove in 2nd gear up a steep canyon for about a full 5 mins continuosly at around 5000rpms!! even with the hood closed, a bright glow of red came from under the car as if there was an underglow kit! Very simple answer. Your exhaust is restricting the flow of exhaust gases.
- Does adding a turbo affect reliability?
- These transmission problems could give the appearance that the addition of a turbo to a car model hurt reliability, but that might not tell the full story. Consumer Reports’ reliability surveys have also found that manufacturers with a lot of experience building turbocharged engines—Audi, BMW, Porsche—tend to have more reliable powertrains.
- Does turbo boost affect gaming performance?
- Yes, Turbo Boost can affect gaming performance a lot. However, since you are asking if it does, it’s safe to say you didn’t notice the performance drop…. QUOTE ME IN A REPLY SO I CAN SEE THE NOTIFICATION! When there is no danger of failure there is no pleasure in success. The CPU can operate well at over 90c, don’t worry about it.
Can a turbo pump water?
Yes. This short video demonstrates how to add air or water cooling to your turbo pump.
- What is the purpose of a turbopump?
- The purpose of a turbopump is to produce a high-pressure fluid for feeding a combustion chamber or other use. There are two types of turbopumps: a centrifugal pump, where the pumping is done by throwing fluid outward at high speed, or an axial-flow pump, where alternating rotating and static blades progressively raise the pressure of a fluid.
- Are turbopumps a problem?
- Turbopumps in rockets are important and problematic enough that launch vehicles using one have been caustically described as a “turbopump with a rocket attached”–up to 55% of the total cost has been ascribed to this area. damaging cavitation to impeller blade surfaces in low-pressure zones.
- What is a turbopump rotodynamic pump?
- A turbopump is a propellant pump with two main components: a rotodynamic pump and a driving gas turbine, usually both mounted on the same shaft, or sometimes geared together. They were initially developed in Germany in the early 1940s. The purpose of a turbopump is to produce a high-pressure fluid for feeding a combustion chamber or other use.
Does a turbo need air?
To increase the airflow further, an air pump (turbocharger) is fitted and compressed air is blown into the engine. This air mixes with the injected fuel allowing the fuel to burn more efficiently so increasing the power output of the engine.
- Do turbo cars work with hot air?
- This indicates that turbo cars don’t work with hot air. The compressed air that’s hot must first be cooled down, before it’s delivered into the combustion chamber for use. This means the argument that says “cold air intake is unnecessary for turbo because turbo cars work with hot compressed air” is absolutely wrong.
- How does a turbo engine work?
- Turbo engine works by ensuring the engine gets more air and gas to generate more power. This means that the engine will work at greater pressures when the turbo boost is on. For this reason, high octane premium gas will be the most appropriate to use for such engines.
- What happens if you run a Turbo without an intercooler?
- Running a turbo without an intercooler will cause extremely hot air to enter the engine – because there’s no intercooler that cools them down before entering the engine. This will definitely cause premature detonation. Aside from engine damages, running a turbo without an intercooler can also cause you to lose horsepower.
- Does cold air intake work on turbo cars?
- Cold air intake does work on turbo cars – it can help you gain minor horsepower (1-5 horsepower) by delivering cool air into the turbo inlet. This means the starting air temperature that gets compressed by the turbo is lower – resulting in an overall lower air temperature when used in the combustion chamber. Hit enter to search or ESC to close 0
Do all turbos need oil?
Turbo systems are made up of moving parts which spin at incredibly high speeds, and work under intense heat and pressure. This means that they need a constant flow of quality engine oil to lubricate the compression valve and intake and outlet fans, to reduce wear and help them perform at their best.

- How much oil does a non-turbo engine take?
- Recommended oil to use on a turbo engine vs. a non-turbo … My Ford Taurus non-turbo takes 5w-20 oil. The turbo version is said to take something like 5w-30.
- Does engine oil affect the performance of a turbo engine?
- Yes it really does. Because turbos spin hundreds of thousands of revolutions and they need really good lubrication. They need a little heavier oil. They need the 30 vs. the 20 and you don’t want to mess with the turbo specifications.
- Do turbocharged cars require more maintenance?
- It depends on the type of maintenance. Turbocharged engines will require more frequent oil changes and fresh spark plugs, though turbo engines typically don’t require additional service compared to naturally aspirated engines. Related: How Often Should I Replace My Spark Plugs?
- What happens if a turbo is not allowed to air?
- If the turbo does not have access to the proper amount of air, excessive restriction will occur and cause: • Oil leakage from the compressor side piston ring, which results in oil loss, a fouled intercooler and potentially smoke out of the tailpipe.
Are turbos faster in the cold?
Yes, compressing air or any gas becomes hot , hot gases expands and contains less oxygen. During cold weather it’s a very noticeable improvement of horsepower.

- Does a turbocharged engine produce more power in colder conditions?
- Thirdly, as per the above analysis an engine will produce more power in colder conditions due to the greater mass of air ingested. If more power is produced and friction stays the same, we would expect a small gain in engine efficiency, too. Finally, let us consider turbocharged engines.
- Should I cool my Turbo before or after a turbo?
- Cooling air into the engine is always going to be a good idea, as heat soak reduces the power of an engine. A turbo does heat air, simply by compressing it, but you will still get a direct benefit from any cooling you can do, either before or after the turbo.
- Does a turbo heat air?
- A turbo does heat air, simply by compressing it, but you will still get a direct benefit from any cooling you can do, either before or after the turbo. This is why any major performance improvements with a turbo tend to end up involving an intercooler. You can also go for more low-tech solutions.
- Why do turbo engines need intercoolers?
- The purpose of this is to cool the air back down to ambient to further increase the mass flow of air into the engine. In conclusion, colder conditions produce a measurable increase in engine power (otherwise intercoolers would not be installed on turbo engines.)






