Turbochargers provide additional horsepower to your petrol-powered engine. They do so by increasing the amount of air and fuel that enters each combustion chamber. Meanwhile, diesel fuel burns at a lower temperature. That causes it to create more exhaust gas, but diesel engines also have higher compression ratings.

- Is a turbo-diesel engine better than a naturally aspirated engine?
- The more efficient the combustion of fuel, the more efficient and powerful the engine. Hence, turbo-diesel engines produce more power and are also fuel-efficient at the same time. Turbochargers also help in generating a superior torque curve as compared to a naturally aspirated diesel engine.
- Can a turbocharger be used in a diesel engine?
- A turbocharger can be used in both petrol and diesel engines. Turbo engines comprise complex parts. If they fail or develop faults, it can impact other engine components. A smaller turbo engine generates the same amount of power as a larger naturally aspirated (NA) engine. Turbochargers are expensive, and the same applies to repair costs.
- What is the difference between a turbo engine and a regular engine?
- The turbo engine is a bit more complicated and if you do not properly maintain the turbocharger, it can leave you when your world is dearer and the repair is not cheap. Higher power: Thanks to the turbocharger, a turbo engine has on average about 25-30% more power than an engine of the same type and capacity.
- What are the benefits of having a turbo on both engines?
- The benefits of having a turbo on either engine are virtually the same, but there are some subtle differences as to how petrol and diesel turbochargers achieve their aim. Some of these differences will alter your driving habits to some extent if you want to extract maximum performance.
- Is 1.0 L turbo engine good?
- What is the disadvantage of turbo engine?
- Why turbo is not used in petrol engine?
- Is diesel really better?
- Is a turbo harder on an engine?
- Are petrol BMW better than diesel?
- Is turbo better on gas?
- Which engines run hotter diesel or petrol?
- Do turbo diesels use more fuel?
- Do turbo cars last less?
- Why are turbo diesels so efficient?
Is 1.0 L turbo engine good?
AC performance is good in 1.0 L engines. For petrol engines, peak power is produced at high rpm whether it’s an NA petrol or turbo petrol. Pickup is because of the torque produced by the engine. 1.0 L produce much more torque than a 1.5L NA engine between 2000-4000 rpm.

- Is a turbocharged car better than a small car?
- Typically speaking, the larger an engine is, the more fuel it will use and the more emissions it will produce. The more emissions a car produces, the more its road tax will cost. If your main focus is low running costs around town, a small car with a 1.0-litre turbocharged engine may be your best bet.
- What are the pros and cons of a turbocharger?
- Turbocharger. With stricter fuel economy standards, more and more cars come with turbocharged engines. With a turbocharger, the vehicle can have a smaller engine and use less fuel when coasting or in stop-and-go traffic. When needed, the turbocharger kicks in and provides extra power. What are the pros and cons of turbo engines?
- What is the difference between a 1.0-litre and a 2.0-litre engine?
- Engines between 1.0- and 2.0-litre are more common amongst larger family hatchbacks and mid-size SUVs. Most engines in this range will be turbocharged and have around 150hp. They often claim to have similar real-world economy figures to smaller 1.0-litre engines.
- What is the difference between a 1.0-litre and a 150hp engine?
- Most engines in this range will be turbocharged and have around 150hp. They often claim to have similar real-world economy figures to smaller 1.0-litre engines. However, cars with larger engines will typically be more expensive than smaller equivalents.
What is the disadvantage of turbo engine?
Disadvantages of a Turbo Engine Well, more power means more energy output per second. This means that you have to put more energy when you use it. So you must burn more fuel. In theory, that means an engine with a turbocharger is no more fuel efficient than one without.
- What are the downsides of a turbocharged engine?
- Five downsides of turbocharged engines are found below. Throttle response is a measure of vehicle responsiveness, which looks at how fast an engine can increase its power output in response to the driver’s request for acceleration. With a turbo engine, you’re waiting for it to spool up to produce torque, or power, to the engine.
- What causes a turbocharger to fail?
- Most failures are caused by the three ‘turbo killers’ of oil starvation, oil contamination and foreign object damage. More than 90% of turbocharger failures are caused oil related either by oil starvation or oil contamination. Blocked or leaking pipes or lack of priming on fitting usually causes oil starvation.
- Is it better to have a turbo or a big turbo?
- And even though the turbocharged engines are made better now, you often have to choose between a small turbo with better response time or a big turbo with more power. Typically, the torque will die off the higher the rpm, creating a waiting period for the boost and feeling of losing power afterward.
- What is the difference between a naturally aspirated and turbocharged engine?
- A naturally aspirated engine is going to have a more linear throttle response than a turbocharged engine, due to the way a turbocharger works and turbo lag, although throttle response is different than turbo lag. “You want a linear relationship between throttle position and the power that’s delivered,” Fenske explains.
Why turbo is not used in petrol engine?
If you attempt to turbocharge a usual petrol engine, its efficiency will reduce drastically. This is because the “back pressure effect’ comes into picture i.e. during the exhaust stroke (considering a 4-s engine), the exhaust gases will suffer some resistance.
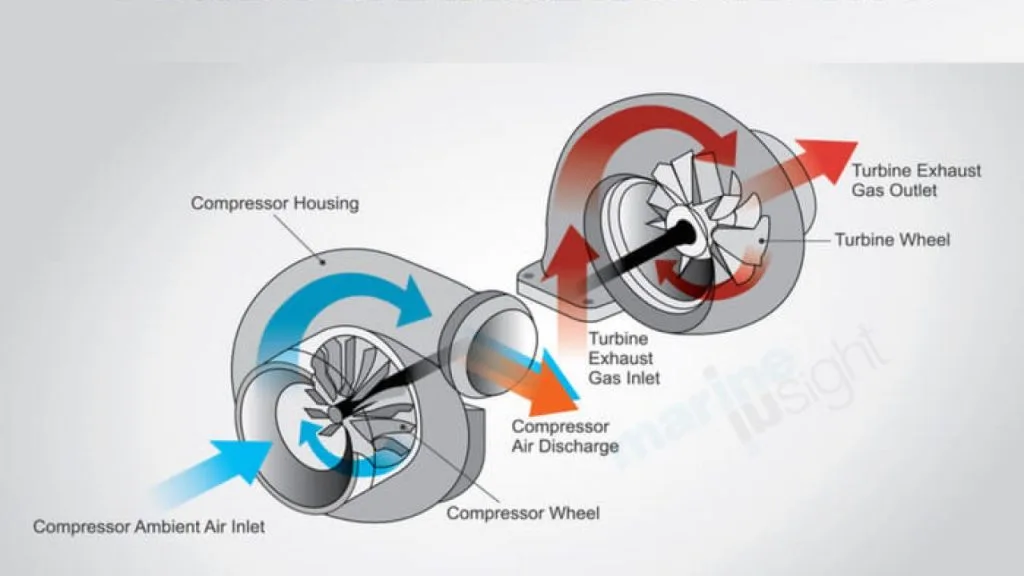
- Why are petrol engines not turbocharged?
- 20–25 years ago petrol engines were not turbocharged because carburetors were common and selling a larger engine was cheaper and easier. Now with all cars being fuel injected and the trend towards smaller more powerful engines with better fuel economy turbocharged petrol engines are becoming much more common. Petrol engines can be turbocharged.
- Do turbos increase power?
- As well as increasing power, turbos increase torque – an engine’s strength – particularly at low revs. That’s useful in small petrol engines which tend to produce not much torque at high revs without a turbo. Naturally-aspirated diesel engines, by contrast, produce a lot of torque at low revs.
- Do you need a turbo on a diesel engine?
- A turbo gives a diesel engine much better top end power. It is pretty much essential to have a turbo on a diesel. A turbo can provide great value on a petrol engine also, but you can be perfectly happy without one. That’s why it seems like they are mostly used on diesels.
- What are the prerequisites for turbocharging an engine?
- So, prerequisite for turbocharging an engine is that the pressure of the exhaust gases should be adequate, which are ofcourse diesel engines (since, the compression ratio is more) or petrol engines with more no. of cylinders ( usually 6 or more). If you attempt to turbocharge a usual petrol engine, its efficiency will reduce drastically.
Is diesel really better?
According to the Department of Energy, diesel motors typically get as much as 35% more miles to the gallon. More torque. The high compression ratio of diesel vehicles generates more torque, making diesel engines a better choice for pulling or hauling lots of weight. More torque.
- Is a diesel engine more efficient than a gasoline engine?
- That is to say, it is not uncommon for a gasoline engine to have two-thirds (⅔) the fuel efficiency of a diesel engine. “DDiesel engines are more fuel-efficient and have more low-end torque than similar-sized gasoline engines, and diesel fuel contains roughly 10% to 15% more energy than gasoline.
- Are diesel engines environmentally friendly?
- But not long ago, diesel engines were thought to be environmentally friendly. What could have gone wrong? Opinion on diesel cars has swung widely over the years. Diesel is a more efficient fuel than petrol, but in the past diesel engines were often noisy and dirty.
- How much better is a diesel engine than a hybrid?
- They typically deliver 25 to 30 percent better fuel economy than similarly performing gasoline engines. Diesels also can deliver as much or more fuel economy than traditional gasoline-electric hybrids, depending on the models involved and whatever rapidly developing automotive technology achieves.
- Is a diesel engine lighter than a gasoline engine?
- To start with, because of their compression ratios compared to gasoline engines, a diesel engine is a lot heavier than a gasoline engine. When trying to cut down on bulky vehicles, lighter engines are often seen as a benefit in terms of performance and efficiency.
Is a turbo harder on an engine?
Turbocharged engines are more demanding on engine oil and work harder than a larger, naturally aspirated engine making similar power.

- What does a turbo do on a car?
- What does a turbo do? A turbo compresses exhaust gas as it exits and sends it back into the engine. The increased airflow sends more fuel into the engine, giving it more power. Using a turbo to get the extra power you need from a smaller engine may seem like a simple way to avoid the downsides of a larger engine.
- Why does a small engine need a turbocharger?
- The first reason is that adding a turbocharger to a smaller engine makes it work harder. The turbocharger increases the pressure and temperature inside the combustion chambers of the engine, which adds more strain on internal components including pistons, valves, and the head gasket. The harder the engine works, the faster it wears out.
- Do turbos produce more power in the same sized engine?
- Turbos produce more power in the same sized engine. That’s because every stroke of the piston generates more power than in naturally-aspirated engines. This means that more cars are now fitted with smaller, turbocharged engines, replacing larger and less economical units.
Are petrol BMW better than diesel?
Benefits of a Diesel Engine The main reason to consider equipping your next BMW with a diesel engine is fuel efficiency. By some estimates, diesel engines are 30 percent more efficient than their gas counterparts. This makes them a particularly good choice for drivers who must deal with long daily commutes.
- Why are diesel cars better than petrol cars?
- Diesel cars give their owners better mpg than their petrol counterparts due to their fuel containing more energy per litre. Lower CO2 emissions. Cars running on diesel produce less carbon dioxide emissions than equivalent petrol cars. High torque.
- What’s the difference between a diesel and a BMW?
- The exact comparisons are done for you by BMW, but we all know they aren’t real world, and in the real world the fuel consumption gap is rather bigger. You do of course have less performance in the diesel, if that’s your thing. That’s the beauty of choice, you can choose.
- Does a diesel engine last longer than a petrol engine?
- Yup. Diesel cars last quite longer than petrol. Some reasons being: Diesel engine parts are generally stronger than gas engine components, and diesel fuel has superior lubricating properties. As a result, diesel engines tend to last twice as long as gas-powered ones. Most gasoline engines convert about…
- How much does a diesel car cost in the UK?
- Below is the list of key points, the importance of which you shouldn’t underestimate: As a general rule, and when buying a diesel car, you will pay a larger amount than you would have for its petrol counterpart. In November 2020, a petrol-powered 1 Series BMW at entry-level, the 118i SE, cost £24,965 in the UK.
Is turbo better on gas?
Fuel efficiency: Because turbochargers give your car extra power without increasing the size of the engine, they’re typically more fuel-efficient than larger engines.
- Do turbocharged engines get better gas mileage?
- The latest turbocharged engines are smaller – in many cases very small. The new Ford Focus and Fiesta ST use 1.0-liter three-cylinder engines. Since the turbocharger only produces extra power and uses extra gas when it needs it, these smaller engines get better gas mileage when the driver is just cruising along than a bigger engine would.
- Does a turbo engine need gas?
- Because turbo engines compress more air in the cylinder, they may pre-detonate and have high chances of knocking. This will have a negative impact on the engine even though modern vehicles have an ECU to compensate for it. It is difficult to ignite premium gas in a turbocharged engine compared to regular gas. What Is the Best Gas for Turbo Engines?
- Why is premium gas a good choice for a turbo engine?
- Premium gas is suitable for turbo engines because it is hard to ignite since it has high octane levels. It is also ideal for running the engine at greater compression rations before detonation. By increasing the compression ratio, a turbocharger boosts the amount of gas in the cylinder, which results in a more efficient engine .
- Do turbochargers really work?
- Since the turbocharger only produces extra power and uses extra gas when it needs it, these smaller engines get better gas mileage when the driver is just cruising along than a bigger engine would. Their tiny turbochargers also spool up to speed quickly – more quickly than the whole engine could rev up to deliver similar power. Do They Work?
Which engines run hotter diesel or petrol?
The greater the compression of a gas, the more heat generated. Because diesel engines have higher compression ratios, they generate more heat. Because diesel engines generate more heat than other combustion engines, they have higher thermal efficiencies.
- Which exhaust is hotter gasoline or diesel?
- For a gasoline engine and a diesel engine of the same power, whose exhaust is hotter? – Quora Answer (1 of 6): Well, petrol engines will have higher exhaust temperatures compared to diesel engines. Why?? Firstly, the expansion ratio (ratio of volume at BDC to volume at TDC) is higher in DE’s compared to PE’s.
- Why do petrol engines have higher exhaust temperatures than diesel engines?
- Answer (1 of 6): Well, petrol engines will have higher exhaust temperatures compared to diesel engines. Why?? Firstly, the expansion ratio (ratio of volume at BDC to volume at TDC) is higher in DE’s compared to PE’s. So, after combustion of air-fuel mixture at TDC the gases expand for much more…
- Why does a diesel engine burn more energy than a petrol engine?
- Diesel fuel can be compressed significantly more before it ignites when compared to petrol, meaning diesel engines can run much higher compression engines than petrols. When the diesel/air ratio does ignite, it expands over a greater range and more energy can therefore be extracted from it.
- Which car brand uses a diesel engine?
- Some examples of car brands using such petrol engines include Ford’s 1.0-litre “EcoBoost” and Nissan’s 1.3-litre “DIG-T.” As mentioned before, diesel cars have higher fuel efficiency than petrol ones. Besides, one litre of diesel fuel has approximately 15% more energy than a litre of petrol.
Do turbo diesels use more fuel?
Diesel power efficiency is slightly higher, hence why diesels can get better fuel economy. Turbos are powered by the normally wasted energy that flows out of the exhaust pipe. A turbo is essentially two fans joined by a common shaft.
- Can a diesel engine be turbocharged?
- As with other engine types, turbocharging a diesel engine can significantly increase its efficiency and power output, especially when used in combination with an intercooler. Turbocharging of diesel engines began in the 1920s with large marine and stationary engines.
- What are the benefits of a turbo engine?
- Lower consumption: because you have a smaller capacity, but a higher power, you can drive in the city without having to overload the engine, so you will have a decent consumption. On the longer drives, the turbo helps you have a higher power at a lower speed, so you won’t have to drive the engine for much longer.
- Is a turbocharged engine better than a non-turbo engine?
- Turbo engines tend to have more problems in many cars, although there are turbocharged engines that are reliable. A turbocharged engine has more components than a naturally-aspirated (non-turbo) motor. These include an exhaust wastegate setup, intercooler, boost control system, vacuum pump and a more complicated crankcase ventilation (PCV).
- Can you use premium gas on a turbo engine?
- When you use premium gas on your turbo engine, it will provide more power compared to using regular gas. However, higher octane would not affect lower-compression engines. These engines will not completely burn the fuel leading to wasted gas. There will be no significant increase in performance when you use premium gas on a regular engine.
Do turbo cars last less?
No. today’s turbochargers are designed to last the lifespan of the vehicle. The truth is, boosted engines require the same amount of maintenance and care that a naturally aspirated engine does.

- Should you drive a turbocharged car?
- Here are the dos and don’ts of driving a turbocharged vehicle. Follow these maintenance and driving tips to ensure you get the full benefit out of your turbocharged engine. Adding in a turbo makes a car’s engine run even hotter than a normal vehicle. For this reason, engines with turbos are more prone to overheating.
- Do turbo cars get more power with a smaller engine?
- So with turbo cars, you get more power with a smaller engine. A feature of the turbocharger is that they’re not always on full blast but get activated only above a certain engine speed. The more the engine rev, the harder they work. It also means that the turbo will start gently during light driving.
- How long does a turbo engine last?
- New turbocharger. That said, there are many turbo engines that are known to last long. Take, for example, the turbodiesel in some Volkswagen cars. We have seen many of them going well past 200K miles with good maintenance. Some other German turbo cars are also known to last with good care.
- Can a turbocharger decrease the lifespan of a car?
- These vehicles began experiencing engine failure once they reached 70,000 miles. Many of these problems were caused by bearing failure, overheating, lack of lubricant, and other issues. With that being said, it is true that a turbocharger can decrease the lifespan of the engine to some degree. More about this matter will be provided below.
Why are turbo diesels so efficient?
In comparison to turbochargers on gasoline engines, diesel turbos are generally setup to a much higher boost pressure, which reduces pumping losses during the intake stroke of the engine, allowing the engine to become more efficient in its conversion of energy through to the crankshaft.

- Are turbo diesel engines better than petrol engines?
- Turbo diesel engines usually out-perform similar sized petrol engines in terms of torque and, quite often, power. The extra torque that diesel engines generate makes them great for carrying big loads and towing. Larger diesel cars often hold their value better than less efficient petrol versions.
- What are the benefits of a diesel engine?
- Vehicles that use diesel engines are generally built with heavy-duty components that can withstand the power of the vehicle, which means less wear and tear on every part of the engine. Diesel engines are also great are self-cooling, which puts them at a significantly-decreased chance of overheating.
- Can a turbocharger be used on a diesel engine?
- The turbocharger was originally intended to be used on diesel engines, since Büchi’s patent of 1905 noted the efficiency improvements that a turbocharger could bring to diesel engines.
- Why is a diesel engine more efficient than an unthrottled engine?
- It’s like sucking through a squashed straw: the engine can’t win but it uses energy trying. The unthrottled diesel engine doesn’t have that problem, which also increases efficiency. On the thorny and controversial question of emissions, the diesel generates less CO2 because it’s more efficient and burns less fuel.






