Fuel efficiency: Diesel is 33% more fuel-efficient than gasoline, and turbochargers further increase diesel fuel efficiency. Improved performance: While ramping up horsepower, they lower emissions and improve altitude compensation. Turbocharging an engine increases the power output of a given engine weight.

- What is a turbo diesel engine?
- The term turbo-diesel, also written as turbodiesel and turbo diesel, refers to any diesel engine equipped with a turbocharger. As with other engine types, turbocharging a diesel engine can significantly increase its efficiency and power output, especially when used in combination with an intercooler.
- What are the benefits of having a turbo on both engines?
- The benefits of having a turbo on either engine are virtually the same, but there are some subtle differences as to how petrol and diesel turbochargers achieve their aim. Some of these differences will alter your driving habits to some extent if you want to extract maximum performance.
- What is the best oil for a turbo diesel engine?
- The Supreme 9000 is a popular choice among turbo diesel owners as it’s an excellent heavy-duty diesel engine oil that provides top-of-the-line protection against deposit formation, wear, soot, and extreme temperature oxidation.
- Are diesel engines good for fuel economy?
- Diesel engines, particularly turbo diesels, provide good fuel economy especially with open road driving – if you do a lot of freeway and highway driving, diesel engines are generally around 20 to 35 percent more economical than the equivalent petrol driven car.
- Why do diesels last longer?
- Why turbo is not used in petrol engine?
- How many km does a turbo last?
- Do turbo diesels use more fuel?
- What kills turbo in diesel?
- Why are turbo diesels so efficient?
- Why do diesels love turbos?
- Why do diesels like turbos?
- Does a TDI have a turbo?
- Why are diesels slower than petrol?
- What can damage turbocharger?
- Can an engine last 30 years?
- Why petrol is more powerful than diesel?
- How many turbos can a car have?
Why do diesels last longer?
In addition to more oil and coolant capacity diesel engines are simply built with heavy duty components that wear out less frequently. Diesel engines are built with a simple yet durable valve train. The rollers are harder and more solid than in gas engines and there are no hydraulic lifter failures to worry about.
- Do diesel engines last longer?
- Nowadays, it’s quite common to see gasoline engines reaching the 200,000-mile mark and still running fine, however, for some reason diesel engines always seem to last significantly longer. Why is that? Stick around for the answer! Do Diesel Engines Last Longer? Yes! Diesel engines do last longer.
- What are the benefits of a diesel engine?
- Vehicles that use diesel engines are generally built with heavy-duty components that can withstand the power of the vehicle, which means less wear and tear on every part of the engine. Diesel engines are also great are self-cooling, which puts them at a significantly-decreased chance of overheating.
- Why don’t we see more diesel engines?
- This is why gasoline-powered engines experience more wear and tear, at lower mileage. Why don’t we see more diesel engines? In 2030, 75% of new vehicles will still have a combustion engine on board.
- Is a diesel engine better than a petrol engine?
- Because diesel engines offer better fuel economy they can be considered to be better for the environment. The emissions they produce are dirtier than a petrol engine, but because you can get more miles for the equivalent volume of emissions they can be considered more environmentally friendly. They perform better.
Why turbo is not used in petrol engine?
If you attempt to turbocharge a usual petrol engine, its efficiency will reduce drastically. This is because the “back pressure effect’ comes into picture i.e. during the exhaust stroke (considering a 4-s engine), the exhaust gases will suffer some resistance.
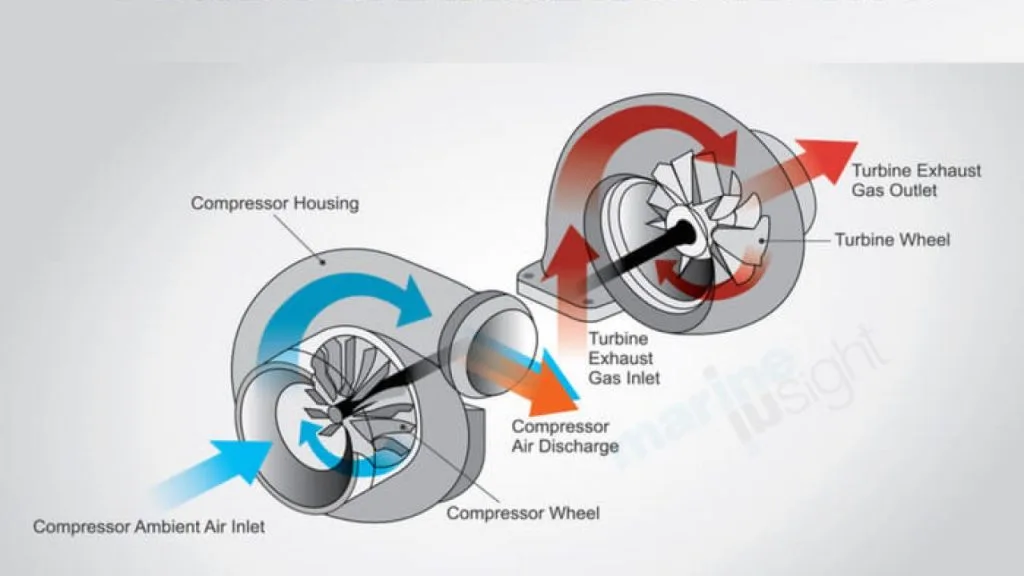
- Why are petrol engines not turbocharged?
- 20–25 years ago petrol engines were not turbocharged because carburetors were common and selling a larger engine was cheaper and easier. Now with all cars being fuel injected and the trend towards smaller more powerful engines with better fuel economy turbocharged petrol engines are becoming much more common. Petrol engines can be turbocharged.
- Do turbos increase power?
- As well as increasing power, turbos increase torque – an engine’s strength – particularly at low revs. That’s useful in small petrol engines which tend to produce not much torque at high revs without a turbo. Naturally-aspirated diesel engines, by contrast, produce a lot of torque at low revs.
- Do you need a turbo on a diesel engine?
- A turbo gives a diesel engine much better top end power. It is pretty much essential to have a turbo on a diesel. A turbo can provide great value on a petrol engine also, but you can be perfectly happy without one. That’s why it seems like they are mostly used on diesels.
- What are the prerequisites for turbocharging an engine?
- So, prerequisite for turbocharging an engine is that the pressure of the exhaust gases should be adequate, which are ofcourse diesel engines (since, the compression ratio is more) or petrol engines with more no. of cylinders ( usually 6 or more). If you attempt to turbocharge a usual petrol engine, its efficiency will reduce drastically.
How many km does a turbo last?
Manufacturers design turbochargers to exceed 300 000 km’s in terms of service in a single lifecycle, however many turbochargers don’t see this due to engine maintenance related issues. Lack of maintenance, late maintenance and incomplete maintenance will all shorten the life of your turbocharger.
- How long does a turbo engine last?
- New turbocharger. That said, there are many turbo engines that are known to last long. Take, for example, the turbodiesel in some Volkswagen cars. We have seen many of them going well past 200K miles with good maintenance. Some other German turbo cars are also known to last with good care.
- How many miles on original Turbo?
- Data point: My 02 Jetta has 287K miles on original turbo. I have 3 general rules: Take it easy on a cold engine: Keep it under about 2400 RPM, but don’t lug it. (Accelerate slowly) until the temp gauge is near normal. Once warmed up, use what’s there. Let it pull through 3000 on upshifts.
- Can a turbocharger decrease the lifespan of a car?
- These vehicles began experiencing engine failure once they reached 70,000 miles. Many of these problems were caused by bearing failure, overheating, lack of lubricant, and other issues. With that being said, it is true that a turbocharger can decrease the lifespan of the engine to some degree. More about this matter will be provided below.
- What is a turbo engine & how does it work?
- Turbocharger. With stricter fuel economy standards, more and more cars come with turbocharged engines. With a turbocharger, the vehicle can have a smaller engine and use less fuel when coasting or in stop-and-go traffic. When needed, the turbocharger kicks in and provides extra power. What are the pros and cons of turbo engines?
Do turbo diesels use more fuel?
Diesel power efficiency is slightly higher, hence why diesels can get better fuel economy. Turbos are powered by the normally wasted energy that flows out of the exhaust pipe. A turbo is essentially two fans joined by a common shaft.

- Can a diesel engine be turbocharged?
- As with other engine types, turbocharging a diesel engine can significantly increase its efficiency and power output, especially when used in combination with an intercooler. Turbocharging of diesel engines began in the 1920s with large marine and stationary engines.
- What are the benefits of a turbo engine?
- Lower consumption: because you have a smaller capacity, but a higher power, you can drive in the city without having to overload the engine, so you will have a decent consumption. On the longer drives, the turbo helps you have a higher power at a lower speed, so you won’t have to drive the engine for much longer.
- Is a turbocharged engine better than a non-turbo engine?
- Turbo engines tend to have more problems in many cars, although there are turbocharged engines that are reliable. A turbocharged engine has more components than a naturally-aspirated (non-turbo) motor. These include an exhaust wastegate setup, intercooler, boost control system, vacuum pump and a more complicated crankcase ventilation (PCV).
- Can you use premium gas on a turbo engine?
- When you use premium gas on your turbo engine, it will provide more power compared to using regular gas. However, higher octane would not affect lower-compression engines. These engines will not completely burn the fuel leading to wasted gas. There will be no significant increase in performance when you use premium gas on a regular engine.
What kills turbo in diesel?
Extreme heat can kill anything, right? Well, the same goes for turbochargers. Prolonged exposure to 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit will eventually take its toll on the turbine (exhaust) side of the turbo.
- Can debris damage a turbocharger?
- Because of the extremely high speeds where turbochargers operate best, introducing debris into the mix can lead to catastrophic turbocharger damage, and can potentially hurt the charge air cooler as well. This isn’t so much an issue of debris from the outside world mingling with the workings of the turbocharger, though.
- How much oil do I need for a turbocharger?
- On larger frame turbos, it’s recommended to use a -6 AN oil supply line (at a minimum) to ensure appropriate oil flow is always on tap. Oil contamination — be it from lack of maintenance, coolant or fuel in the engine oil or debris from an internal engine component breaking down — can wreak havoc on a turbocharger as well.
- Why do turbocharged engines burn out?
- The shaft material can thus burn out and break due to the friction between the shaft and the bearings. Fortunately for those running turbocharged engines – particularly in OEM applications – the formula for damage prevention is pretty straightforward.
Why are turbo diesels so efficient?
In comparison to turbochargers on gasoline engines, diesel turbos are generally setup to a much higher boost pressure, which reduces pumping losses during the intake stroke of the engine, allowing the engine to become more efficient in its conversion of energy through to the crankshaft.
- Are turbo diesel engines better than petrol engines?
- Turbo diesel engines usually out-perform similar sized petrol engines in terms of torque and, quite often, power. The extra torque that diesel engines generate makes them great for carrying big loads and towing. Larger diesel cars often hold their value better than less efficient petrol versions.
- Can a turbocharger be used on a diesel engine?
- The turbocharger was originally intended to be used on diesel engines, since Büchi’s patent of 1905 noted the efficiency improvements that a turbocharger could bring to diesel engines.
- Why is a diesel engine more efficient than an unthrottled engine?
- It’s like sucking through a squashed straw: the engine can’t win but it uses energy trying. The unthrottled diesel engine doesn’t have that problem, which also increases efficiency. On the thorny and controversial question of emissions, the diesel generates less CO2 because it’s more efficient and burns less fuel.
Why do diesels love turbos?
This is where the turbocharger is critical to the power output and efficiency of the diesel engine. It is the job of the turbocharger to compress more air flowing into the engine’s cylinder. When air is compressed the oxygen molecules are packed closer together.
- Why do I need a turbo?
- Put the turbo on, and boom, you got some power. Diesels are bent toward having more torque. The turbo allows the diesel engine to have some get up and go under acceleration. The added horsepower makes the diesel usable on the road. Without it, the diesel would not be fit to drive on the road. It could be very dangerous.
- What would happen if a diesel engine didn’t have turbos?
- Without it, the diesel would not be fit to drive on the road. It could be very dangerous. You need the power to be able to pull out on the road and not cause an accident. Without turbos, diesels would not have hardly any horsepower at all. They need help, and together, they become great.
- Do diesel engines spin high RPM?
- When looking at diesel engines they tend to not spin high rpms. I have not seen to date a light-duty truck engine that comes with a red-line above 5,000 rpm. To add to that, the average performance turbo diesels also do not operate above 4,000 rpm.
Why do diesels like turbos?
Turbochargers offer a number of benefits, including: Fuel efficiency: Diesel is 33% more fuel-efficient than gasoline, and turbochargers further increase diesel fuel efficiency. Improved performance: While ramping up horsepower, they lower emissions and improve altitude compensation.

- Do all diesel engines have turbos?
- Not all diesels have turbos. There are diesel engines that are naturally aspirated. This means that they rely completely on atmospheric pressure for air induction. These engines have substantially less power. But all modern diesel engines have turbos. While not all diesels have a turbo. All modern diesels do.
- What are the modern advancements in diesel turbocharging?
- Look out for a future blog post on the modern advancements in diesel turbocharging. With petrol engines, the addition of a turbo is all about increasing engine power, so the goal is to increase the pressures inside the combustion chamber.
Does a TDI have a turbo?
The first part of the TDI moniker is relatively straightforward – it stands for ‘Turbocharged’, indicating that the car has a turbocharger fitted to its engine.
Why are diesels slower than petrol?
Diesel engines, because of the weight and compression ratio, tend to have lower maximum RPM ranges than gasoline engines (see Question 381 for details). This makes diesel engines high torque rather than high horsepower, and that tends to make diesel cars slow in terms of acceleration.
- Why do diesel engines operate at lower speeds than petrol engines?
- Diesel engines generally operate at lower speeds than petrol engines primarily because the less volatile fuel takes longer to burn. The higher cylinder pressures also require more robust construction and the higher compression ratios necessitate longer crank stroke, both of which result in reduced engine speeds.
- Why are diesel engines so expensive?
- Diesel engines also tend to be more expensive. Diesel engines, because of the weight and compression ratio, tend to have lower maximum RPM ranges than gasoline engines (see Question 381 for details). This makes diesel engines high torque rather than high horsepower, and that tends to make diesel cars slow in terms of acceleration.
- Is a diesel engine better than a heat engine?
- In fact, including the energy advantage of the fuel itself, diesels are up to 40% more efficient at doing that. Both types of engines are classified as ‘heat’ engines because they convert heat energy from fuel into mechanical energy.
- Do diesel engines get better MPG?
- As a long time diesel owner, I know for a fact that engines of similar size but are diesel generally get higher mpg and don’t require a lot of the maintenance (tune ups, etc) that gas engines do. In Europe, there is a higher prevelance of diesel cars not only for the higher mpg but that its cheaper than regular gas.
What can damage turbocharger?
Most failures are caused by the three ‘turbo killers’ of oil starvation, oil contamination and foreign object damage. More than 90% of turbocharger failures are caused oil related either by oil starvation or oil contamination. Blocked or leaking pipes or lack of priming on fitting usually causes oil starvation.

- What should you never put in a turbocharger?
- Such items include loose bolts, injection nozzle fragments, compensator bellow bits, welding electrode stumps, wrenches and screwdrivers, rags or any other foreign objects. Due to the extreme service speed of a turbocharger, even minute particles may damage vital parts and lead to severe damage.
- Can sand damage a turbocharger?
- You can imagine that at those speeds, damage accumulates incredibly quickly. Since the tips of the blades move at a speed of around 2000 km/h, any object that enters the turbochargers, even as small as grains of sand, can damage a turbocharger enough to make it perform incorrectly or fail instantly.
- What happens if you put oil in a turbocharger?
- This will cause the remaining oil in the turbocharger to “soak” the heat increasing the likelihood of oil coking which means that the oil will burn and leave particles in the bearing system and on the shaft. This will damage the bearings and the cartridge could become noisy due to this. TIP!
Can an engine last 30 years?
But an amazing fact is that diesel engines can run for 1,000,000-1,500,000 miles before needing any major diesel repairs. If kept well-maintained, a diesel engine can be driven for about 30 years or more.
- How long do engines last?
- As you are really curious about how long do engines last, we would say there is no absolute rule when it comes to how long engines will last. But the average lifespan is around 8-9 years or 150.000 – 170.000 miles. The new model of cars with the innovation has leveraged the longevity of the engine to 10 years or 200.000 miles in equivalent.
- How long does a car last?
- The top 15 long-lasting models identified each have over 3.0 percent of their vehicles (more than two-and-a-half times the overall average) reach 200,000 miles, and include a mix of vehicle types with 9 SUVs (including a hybrid), three pickup trucks , one sedan, two minivans, and one hybrid hatchback.
- What factors affect the lifespan of a car engine?
- The first factor that affects your car engine lifespan is what it is made from. Car engines are made of several different metals, but some of the most common are iron and aluminum. In fact, some engines are made of the combination of 2 or more metals. Many trucks have engines with iron blocks and aluminum heads.
- How long should you let your car idle?
- As a general rule for turning off your vehicle, don’t let your car idle for more than 10 seconds. Doing so will cost you more fuel than stopping and starting your car up again. Also, it helps the environment by not letting toxic fumes out into the atmosphere.
Why petrol is more powerful than diesel?
Diesel and petrol engines The calorific value of diesel fuel is roughly 45.5 MJ/kg (megajoules per kilogram), slightly lower than petrol which is 45.8 MJ/kg. However, diesel fuel is denser than petrol and contains about 15% more energy by volume (roughly 36.9 MJ/litre compared to 33.7 MJ/litre).
- Why do petrol engines have a higher power than diesel engines?
- So due to higher RPM operation petrol engines have a higher power even though they might have relative less torque compared to diesel engines. since Power is directly proportional to the Engine Speed. The calorific value of diesel fuel is roughly 45.5 MJ/kg (mega joules per kilogram), slightly lower than petrol which is 45.8 MJ/kg.
- What is the difference between gasoline and diesel?
- Petrol and diesel are petroleum-derived liquid mixtures used as fuels. Though both have similar base product but have different properties and usage. More than gasoline (petrol). Diesel fuel produces approximately 13% more CO2 gas per gallon of fuel burned, compared to gas (petrol) engines. Lower than diesel.
- Why is diesel a more environmentally friendly fuel?
- Diesel was promoted as a more environmentally friendly fuel as part of the EU’s response to the 1997 Kyoto Protocol to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, especially carbon dioxide (CO₂). Diesel engines are “lean-burn”, meaning they use less fuel and more air to get the same performance as a petrol engine.
- Are petrol cars more reliable than diesel?
- Yes, according to statistics, diesel cars are three times more likely to break down with time than their petrol counterparts and can cost 20% more to repair. Yet, diesel engines prove to last longer than their petrol counterparts.
How many turbos can a car have?
Automobile manufacturers rarely use more than two turbochargers.






