Oldsmobile Jetfire
The first turbocharged cars were the short-lived Chevrolet Corvair Monza and the Oldsmobile Jetfire, both introduced in 1962. Greater adoption of turbocharging in passenger cars began in the 1980s, as a way to increase the performance of smaller displacement engines.

- What was the first turbocharged car?
- In fact, a lot of early turbocharged cars were European – cars such as the Porsche 930, Saab 99 Turbo and the BMW 2002 Turbo. However, the first car to ever get boost was as American as apple pie. Back in 1962, General Motors decided that the 3.5-litre V8 under the hood of the Oldsmobile Cutlass just didn’t have enough power.
- What was the first Saab Turbo?
- In 1978, the Saab 99 had offered the first turbo on a production car since G.M.’s misfires. “The very first Saab turbos were not reliable cars,” said Jim Smart, owner of the Saab specialist Smart Motors in Santa Fe, N.M.
- What happened to turbos in the 1960s?
- In the 1960s it was exotic, it was innovative, and for G.M. it was — above all — a disaster. The Olds F-85 Jetfire and the Chevy Corvair Monza Spyder were America’s first mass-produced turbocharged passenger cars, and they were such technological and commercial flops that Detroit would shun turbos for years to come.
- What is a turbocharger in a car?
- Turbochargers for passenger cars gained popularity in the 1980s, with the first models being the Chevrolet Corvair Monza and Oldsmobile Jetfire in 1962. The main components of a turbocharger include a turbine, compressor, and center housing hub rotating assembly.
- How many turbos can a car have?
- At what rpm is turbo activated?
- Why turbo is not used in petrol engine?
- Who invented turbo?
- What is the difference between a turbo and supercharger?
- Does a turbo make a car faster?
- Was Saab the first turbo car?
- What was the first turbo BMW?
- What was the first f1 with turbo?
- Is there a twin turbo?
- How to test car battery?
- Can you turbo a gas engine?
- Did Renault invent turbo?
- What was the first German car with a turbo?
How many turbos can a car have?
Automobile manufacturers rarely use more than two turbochargers.

- Do all cars have turbo?
No not all cars have turbo. A turbo charger is a small round device normally mounted in the exhaust stream near the engine. The expelled exhaust gases spin a turbine that powers a fan to force air into the engine. In a naturally aspirated engine the air would have to be pulled in to the cylinder during the intake stroke.
You won’t find many city cars with turbos, and the cheapest engines in superminis – cars like the Seat Ibiza and Vauxhall Corsa – tend to be naturally aspirated, another way to describe non-turbocharged engines.
- Are turbochargers bad for your engine?
- As above, a car that is built to include the use of a turbocharger will be the best option if you’re looking for boost. However, if you do wish to install a turbo in your car without upgrading the other aspects of the vehicle, then you will put more strain on the engine and potentially break it.
- How much horsepower does a turbo boost?
- A turbo can boost an engine’s horsepower by 30 to 40 percent or approximately 70 to 150 HP. Is a turbocharger bad for your engine? A turbocharger adds the danger of knocking, as when you compress air, the temperature increases, which can damage the engine if you don’t reduce the compression ratio.
- Why do we use a turbo on a smaller engine?
- Vehicle manufacturers use a turbo on a smaller engine to improve the fuel economy of a car without losing power. A smaller engine is going to be more fuel efficient than a larger engine. The added turbo allows the smaller engine to produce the same amount of power as a larger engine.
At what rpm is turbo activated?
You Spin Me Right Round (Like a Turbo, Baby): The turbine in a typical car turbocharger has to spin incredibly quickly. While your car’s engine revs, at cruise, at around 2,000 rpm, a turbo’s turbine can reach rotational speeds of more than 280,000 rpm.
- Is a turbo activated?
- a turbocharger is not “activated.” the turbine spins freely with the exhaust gas. As long as the engine is turning, the turbo will turn in kind. Unless the turbocharging system is valved so it can be isolated, but nobody does that! Are auto Turbos on all the time?
- How many RPM does a turbo get?
- A decent turbo hits full boost at 3k rpm, but it varies depending on the mechanical efficiency of the turbo and how much exhaust is being put out. Three years of Bible school, 40+ years in the working world. Author has 24.4K answers and 9.1M answer views 5 y That will depend on the load on the engine.
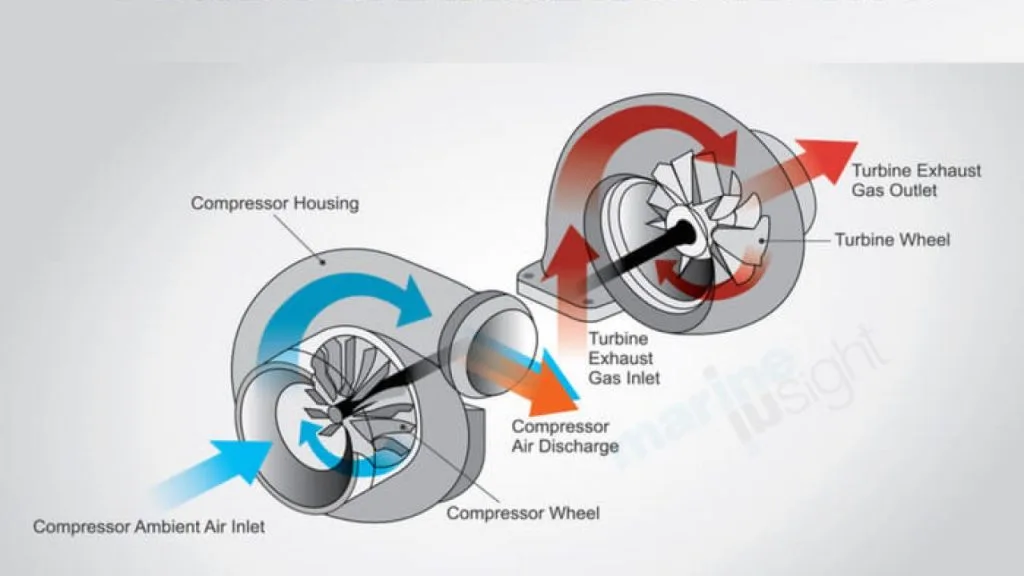
- How does a turbocharger work?
- A turbocharger is a turbine-driven forced induction machine that boosts the efficiency and power output of an internal combustion engine by bringing additional air into the combustion chamber. If it seems a bit complicated to understand how a turbo works, take the cue from the fact that an engine run by a mixture of fuel and air.
- How long does it take for a turbo to kick in?
- Turbo will not kick in until it reaches a certain RPM, usually between 1200 to 1500 rpm. Exhaust gasses power the Turbo system, and it takes time for the car to generate enough exhaust gas to power the turbo system. The lag is a normal phenomenon for turbocharged engines. However, it is possible to speed up or eliminate the lagging period.
Why turbo is not used in petrol engine?
If you attempt to turbocharge a usual petrol engine, its efficiency will reduce drastically. This is because the “back pressure effect’ comes into picture i.e. during the exhaust stroke (considering a 4-s engine), the exhaust gases will suffer some resistance.
- Why are petrol engines not turbocharged?
- 20–25 years ago petrol engines were not turbocharged because carburetors were common and selling a larger engine was cheaper and easier. Now with all cars being fuel injected and the trend towards smaller more powerful engines with better fuel economy turbocharged petrol engines are becoming much more common. Petrol engines can be turbocharged.
- Do turbos increase power?
- As well as increasing power, turbos increase torque – an engine’s strength – particularly at low revs. That’s useful in small petrol engines which tend to produce not much torque at high revs without a turbo. Naturally-aspirated diesel engines, by contrast, produce a lot of torque at low revs.
- Do you need a turbo on a diesel engine?
- A turbo gives a diesel engine much better top end power. It is pretty much essential to have a turbo on a diesel. A turbo can provide great value on a petrol engine also, but you can be perfectly happy without one. That’s why it seems like they are mostly used on diesels.
- What are the prerequisites for turbocharging an engine?
- So, prerequisite for turbocharging an engine is that the pressure of the exhaust gases should be adequate, which are ofcourse diesel engines (since, the compression ratio is more) or petrol engines with more no. of cylinders ( usually 6 or more). If you attempt to turbocharge a usual petrol engine, its efficiency will reduce drastically.
Who invented turbo?
Alfred Buchi
Alfred Buchi, a Swiss engineer, put forward the first plans for a supercharger driven by exhaust gases, and the turbo was born. In 1905, he patented the idea, and in 1915, whilst working as the Chief Engineer for the research wing of Sulzer Brothers, he built the first turbocharged diesel engine.
- Who invented the turbocharged engine?
- R. Diesel & G. Daimler. The history of the turbocharged motor is almost as old as the invention of the internal combustion engine itself. In this time Gottlieb Daimler (1885) and Rudolf Diesel (1896) attempted by precompression of the air supplied to the engine the engine power increase and fuel consumption to be reduced.
- What is a turbo generator?
- Turbo generators are used for high shaft rotational speeds, typical of steam and gas turbines. The rotor of a turbo generator is a non-salient pole type usually with two poles. The normal speed of a turbo generator is 1500 or 3000 rpm with four or two poles at 50 Hz (1800 or 3600 rpm with four or two poles at 60 Hz).
- Who invented the VNT turbocharger?
- The head of the laboratory for aviation (DVL) in Berlin Dr. Werner Theodor von der Nuell starts in 1936 with the development of the VNT turbocharger. After the end of World War II, a small group of former BMW employees began under the leadership of Dr. Müller in the WMF (Württembergische Metallwarenfabrik) to build a VNT turbocharger.
What is the difference between a turbo and supercharger?
Turbochargers use the vehicle’s exhaust gas; two fans – a turbine fan and a compressor fan – rotate from exhaust gas. Conversely, superchargers are powered directly by the engine; a belt pulley drives gears that cause a compressor fan to rotate.
- Is a turbocharger better than a supercharger?
- Finally, most turbochargers provide a better total increase in horsepower than superchargers, because their speed can be changed by adjusting the waste gate (which is sometimes an automatic function). Most turbochargers suffer from lag.
- What is a turbocharger and how does it work?
- – Gabriella Your turbocharger is a turbine/fan device driven by the engine’s exhaust gases, devised to boost the pressure of the incoming air into the engine. This pressure boost is referred to as “forced induction” and is used to improve engine efficiency and power output.
- What is the difference between twin turbo and twincharger?
- A twin turbo is very different from a twincharger. Twincharging refers to an engine that features both a turbo and supercharger, as seen with some Volvo motors. What is a Supercharger? With the supercharger, you notice an air compressor design which increases the density and pressure of the air forced into an internal combustion engine.
- What is a supercharger in a car?
- The supercharger is a common feature in most speed-oriented vehicles, like sports cars, as it helps boost their power. It is an air compressor whose primary role is to boost the density and pressure of air entering the engine. The more air that gets into the engine, the more fuel it takes for ignition, translating to more power.
Does a turbo make a car faster?
Do turbo engines make your car faster? A turbocharger forces more air into the engine and increases the horsepower produced. As a result, you will get a much faster and more powerful drive.
Was Saab the first turbo car?
The Saab 99 Turbo was one of the first ‘family cars’ to be fitted with a turbo after the 1962-63 Oldsmobile Turbo Jetfire; other contemporary turbocharged automobiles were ‘specialised’ vehicles and were difficult to drive.

- What is a Saab Turbo?
- The Saab Turbo was ther first convetional family car that was powered by a turbocharged petrol turbo engine developed along entirely new principles. Saab’s turbo engines have undergone very intensive testing – on the test bench, each prototype turbo engine has passed a 5,000-hour test, equivalent to 600,000 kilometers
- What was the first Saab car?
- Saab 92001 or Ursaab: The prototype for the first Saab production car (1946) Saab Prometheus: A 9000 fitted with a joystick instead of a steering wheel (1993) 1958: The GT 750 is the first Saab car fitted with seatbelts as standard. 1963: Saab becomes the first volume maker to offer diagonally split dual brake circuits.
- What is a Saab 99?
- The Saab 99 is a car which was produced by Saab from 1968 to 1984; their first foray into a larger class than the 96. While considered a large family car in Scandinavia, it was marketed as a niche compact executive car in most other markets.
What was the first turbo BMW?
BMW 2002 turbo E20
The first of its kind. BMW 2002 turbo E20. The first of its kind. In 1973, the BMW 2002 turbo celebrated its debut, while the world watched the oil price with bated breath as it climbed ever higher. Nobody knew where it would end.
- When did BMW start using a turbocharged engine?
- BMW’s first mass-production turbocharged petrol engine was the six-cylinder BMW N54, which debuted in the 2006 E92 3 Series 335i model. In 2011, the F30 3 Series was released, with turbocharged engines being used on all models. This shift to turbocharging and smaller engines was reflective of general automotive industry trends.
- Who designed the BMW E25 Turbo?
- The E25 Turbo concept sports car was built by BMW as a celebration for the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich. It was designed by Paul Bracq, with gullwing doors and was based on a modified 2002 chassis with a mid-mounted engine.
- What was the BMW 2002 Turbo?
- The BMW 2002 Turbo was the fastest and most desirable version of what was arguably the Bavarian automakers most important fast saloon car – The BMW 2002. The fundamental design ethos of the BMW 2002 would lay the foundation for the company and help establish its reputation for building “driver’s cars” that extends all the way to the modern day.
- What was the first car made by BMW?
- The 1978 BMW M1 was BMW’s first mid-engined sports car and was developed in conjunction with Lamborghini. It was also the first road car produced by BMW’s motorsport division, BMW M. In 1980, the M division produced its first model based on a regular production vehicle, the E12 5 Series M535i.
What was the first f1 with turbo?
Turbo technology revolutionizes Formula 1 First trialed during the 1977 season, it achieved success two years later.

- What was the first turbocharged car to race in F1?
- Resplendent in Renault’s corporate yellow, white and black and driven by Jean-Pierre Jabouille (who, incidentally, also designed the car) Renault’s RS01 made history at Silverstone that day as the first turbocharged car to race in F1. Powered by a 1.5-litre V6 Renault Gordini engine, the RS01 quickly became a joke in pitlane.
- What is a Formula One engine?
- This article gives an outline of Formula One engines, also called Formula One power units since the hybrid era starting in 2014. Since its inception in 1947, Formula One has used a variety of engine regulations. “Formulae” limiting engine capacity had been used in Grand Prix racing on a regular basis since after World War I.
- What was the first Formula 1 race?
- There is some debate as to what can be considered to be the first Formula 1 race. The first race under the new regulations was the 1946 Turin Grand Prix held on 1 September, the race being won by Achille Varzi in an Alfa Romeo 158 Alfetta – but this was before the Formula was officially in place.
- When did Formula One start using a Cooper engine?
- Powered by undersized engines, the Coopers remained outsiders in 1958 but as soon as the new 2.5-litre Coventry-Climax engine was available, the little British cars went on to dominate Formula One.
Is there a twin turbo?
Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case of a direct-injection engine).
- Is a twin-turbo better than a single turbocharger?
- Both systems have their merits, but the benefit of a twin-turbo is that it has the potential for reductions in turbo lag compared to one single turbocharger doing all the work. The twin-turbo delivers lower boost pressures to reduce turbo lag, but the combination of the two turbines creates plenty of power.
- What is a parallel twin-turbo engine?
- The aim of using parallel twin-turbos is to reduce turbo lag by being able to use smaller turbochargers than if a single turbocharger was used for the engine. On engines with multiple cylinder banks (e.g. V engines and flat engines) use of parallel twin-turbos can also simplify the exhaust system.
- What are the different types of turbochargers?
- There are many different ways of turbocharging a car. The terms bi-turbo, twin-turbo, twin-scroll turbo, ball-bearing turbo, journal-bearing turbo, and hybrid turbo are all terms that turbo fans are familiar with. Here is a breakdown of the various types of turbochargers available:
How to test car battery?
- How to test a car battery with a multimeter?
- Testing a car battery with a multimeter is a simple process. The first thing to do is make sure you can access the two terminals on the top of the car battery.
- How can you tell if your car battery is fully charged?
- For this test you need a car battery tester. Test your battery with a CCA rating of one and a half and observe if the battery holds 9.6 volts for 15 seconds. When performing the test, make sure the battery is fully charged. 5.
- How do you test a starter battery?
- In order to test your battery against the load of its starter, you need to make sure it has a strong connection that’s not interfered with by oxidized terminals or a poor connection. If the cables can move at all on the terminal, they’re loose and need to be tightened.
- How to load test a battery?
- I will show you how to use a load tester to load test your batteries. So let’s run through this real quick, just like any car, we’re going to start by removing the negative terminal first and then the positive terminal. Connect the tester to the battery. Positive to the positive, negative to the negative. Choose your battery parameters.
Can you turbo a gas engine?
As emission regulations became stricter, the application of turbochargers provided a perfect solution for downsizing by reducing the fuel consumption without penalty in engine performance and drivability. The concept of turbocharging is fundamentally the same for gasoline and diesel engines.

- Can you put regular gas in a turbo engine?
- Yes but, turbocharged engines run at a higher compression ratio, therefore they need higher octane, most likely it will run poorly on regular gas. Father, Dentist, Pro-EV/Cleantech, hard drive recycler.
- What is a turbocharged car?
- Turbos are taking the auto world by storm. Over one-third of newly manufactured light-duty vehicles come turbocharged. That means many people have a turbocharged vehicle and don’t even know it! Turbocharged vehicles pack a real punch, but with extra power comes extra responsibility.
- Should I buy a non-turbo or a turbocharged car?
- So while many modern-day turbocharged cars don’t have particularly unreliable engines, you may want to stick with a non-turbo (sometimes call naturally aspirated) vehicle if you want peace of mind that the engine is going to last a very long time.
- How does a turbo engine affect a car?
- Because turbo engines compress more air in the cylinder, they may pre-detonate and have high chances of knocking. This will have a negative impact on the engine even though modern vehicles have an ECU to compensate for it. It is difficult to ignite premium gas in a turbocharged engine compared to regular gas.
Did Renault invent turbo?
While the term ‘turbocharging’ would gain currency much later, with the patent, Louis Renault had opened the doors to an exciting new world. The first turbochargers were used by Renault not in cars, but airplanes.
- When did Renault introduce a turbo engine?
- Renault introduced the turbo engine to Formula One when they debuted their first car, the Renault RS01 at Silverstone in 1977. The Renault team continued until 1986. From 1989 Renault supplied engines for the successful Williams-Renault car.
- How were Grand Renault engines made?
- The Grand Renaults were built using a considerable amount of aluminium. Engines, brakes, transmissions, floor and running boards and all external body panels were aluminium. Of the few that were built, many went to scrap to aid the war effort. In 1931, Renault introduced diesel engines for its commercial vehicles.
- When were Renault cars made?
- For example, a “1927” model was mostly produced in 1928. Renault cars during this time period had two model lines; the economy four-cylinder engine models that in the 1930s became the suffix “Quatre” and the luxury six-cylinder models that were initially sold with the suffix “-six” that later became the suffix “Stella”.
What was the first German car with a turbo?
The turbocharger first appeared at the 24 Hours of Le Mans in 1974 on a Porsche, before the 1976-78 period produced a series of turbocharged face-offs between the German manufacturer and Renault.
- When did BMW start using turbochargers?
- Indeed, BMW is the first manufacturer in Germany who brought 1973 the “2002 turbo” on the market. High engine power, but high fuel consumption coupled with a low reliability brought this era of fast. Driven by the oil crisis in 1973, the commercial use of turbochargers for diesel engines enforced.






